[Day 216] Pipelines for XGBoost and CatBoost training, and using the models in the real-time inference pipeline
Hello :)
Today is Day 216!
A quick summary of today:- created pipelines to train XGBoost and CatBoost models
- added XGBoost and Catboost models' predictions in the real-time inference pipeline
- update model dictionary UI
- created project README
The project submission deadline is 11th of Aug, and after that we will make the repo public, but until then I just have to share pictures from the project.
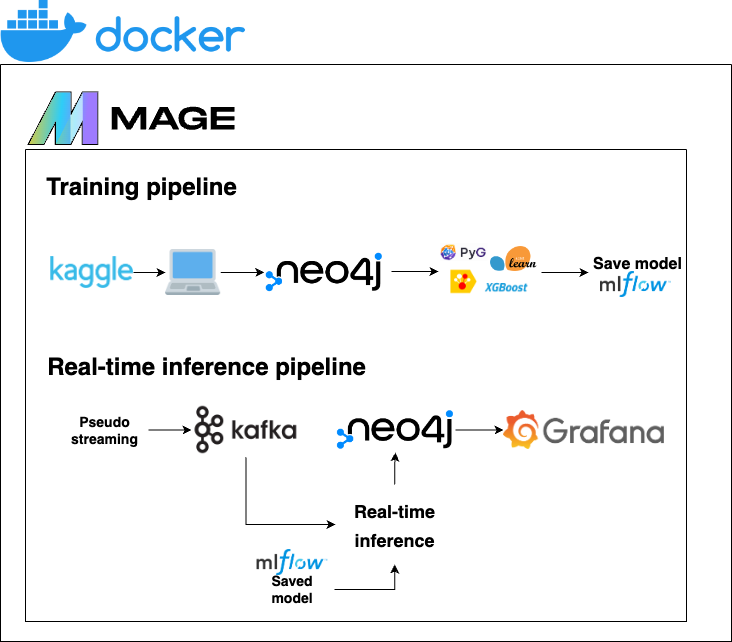
All pipelines including today's:
Setting up model training pipes was easy, the tricky part was using the models. Because the models require OHE data (or dummy vars), so the approach I ended up with was from the development notebook, I took all the columns that are used for the model training data, to emulate a OHE dataset, then I created a dict with key: col, value:0. When a message gets processed, the code goes over the data, and updates the 0 to a 1 if a particular value is there. It is easier to understand with an example - if the transaction has category: entertainment, then in the dictionary, the key category_entertainment gets a value of 1 - and the same for all others. Then this dictionary is used as input for the XGBoost and CatBoost models. It might not be the most elegant solution, but it works.
Next, I updated the model dictionary streamlit UI
Now, it automatically reads folders that start with models_. This is not that great, the best would be to read artifacts for each model from mlflow, but given this is all local, it is fine. Later, after the submission, when I do some extra work on this project I might setup mlflow to run on GCP, and use a proper artifact and backend store. Now the UI provides info like:
Finally, I set up a project README
It'd be best for me to just share a link to it, but again - the repo is private for now.
Project overview
- Kaggle - Transaction data is taken from here
- Docker - used for containerization to ensure that the application is consistent across different environments
- Mlflow - used for easy model comparison during development
- Model training - models are trained using a combination of libraries: sklearn, xgboost, catboost, PyG
- Mage - used for pipeline orchestration of the model training and real-time inference pipelines
- Neo4j - used as a Graph database to store transaction data as nodes and edges
- Kafka - used to ensure real-time transaction processing
- Grafana - used for real-time dashboard creation and monitoring
- Streamlit - used to host a model dictionary showing models, evaluation metrics, and feature importance graphs
Real-time inference pipeline
To simulate real-time information, we use the Kaggle fraudTest.csv dataset and send 5 transactions every second through Kafka. The transactions are received and new columns, where the models predict not fraud/fraud, are created. This data is sent to neo4j and used in the Grafana dashboard, which updates every 5 seconds with the latest information.
Monitoring
Information from Neo4j is extracted and visualised through a real-time dashboard in Grafana
Future improvements
- Use a cloud provider for the following services (and use Terraform to serve the resources):
- MLflow database and artifact store
- Mage
- Use the official cloud option for:
- Neo4j database
- Grafana
- Deploy Streamlit for improved accessibility
- Add unit/integration tests
- Load models from Mlflow in the model dictionary
There is also a section on Reproducability, but I will share that once the repo is public.
That is all for today!
See you tomorrow :)