[Day 196] Learned about 'ML canvas' and more about MLOps
Hello :)
Today is Day 196!
A quick summary of today:- Today I found this great resource for MLOps. Below I will summarise the posts I read
A better pic of the above is on my repo. I learned about the above 'ML Canvas' concept from the below resources.
Motivating MLOps
Why MLOps?
Machine learning (ML) models are increasingly being used in production environments, but their development and deployment are often disconnected from traditional software development and operations practices. This disconnection leads to various pain points, such as:
- Lack of collaboration: Data scientists, engineers, and operators work in silos, leading to inefficiencies and errors.
- Inconsistent workflows: Ad-hoc processes and manual interventions hinder reproducibility, scalability, and maintainability.
- Inadequate infrastructure: Insufficient infrastructure and tools lead to difficulties in deploying, monitoring, and updating ML models.
Motivation for MLOps
To address these challenges, MLOps aims to bridge the gap between ML model development and deployment by:
- Streamlining workflows: Automating and standardizing ML workflows to improve efficiency, reproducibility, and collaboration.
- Improving infrastructure: Providing scalable, secure, and efficient infrastructure for ML model deployment and management.
- Enhancing collaboration: Fostering collaboration between data scientists, engineers, and operators to ensure seamless ML model development and deployment.
By adopting MLOps, organizations can:
- Increase productivity: Reduce time-to-market and improve resource utilization.
- Improve model quality: Enhance model accuracy, reliability, and explainability.
- Reduce risks: Minimize errors, bias, and security vulnerabilities.
Designing ML-powered Software
Phase Zero: Problem Formulation
Phase Zero is the initial stage of the Machine Learning Operations (MLOps) lifecycle, focusing on problem formulation. This phase is crucial in setting the foundation for a successful ML project. The primary goal of Phase Zero is to define a problem worth solving and identify the opportunities where machine learning can add value.
Key Activities:
- Problem Identification: Identify business problems or opportunities that can be addressed using machine learning.
- Stakeholder Alignment: Engage with stakeholders to understand their needs, expectations, and constraints.
- Problem Formulation: Clearly define the problem, including the objectives, key performance indicators (KPIs), and success metrics.
- Data Exploration: Initial exploration of available data to understand its quality, relevance, and potential for ML model development.
- Feasibility Study: Assess the technical feasibility of the project, including the availability of resources, data, and infrastructure.
Deliverables:
- Problem Statement: A clear, concise description of the problem to be addressed.
- Project Charter: A document outlining the project's objectives, scope, stakeholders, and timelines.
- Initial Data Report: A summary of the initial data exploration, highlighting data quality, relevance, and potential issues.
Best Practices:
- Involve Stakeholders Early: Engage with stakeholders throughout the problem formulation phase to ensure their needs are met.
- Be Iterative: Be prepared to refine the problem statement and project charter as new information becomes available.
- Keep it Simple: Focus on a specific, well-defined problem to increase the chances of success.
There is this very nice 'ML canvas' that once filled can provide an overview of the project, and I might do it for my MLOps zoomcamp project.
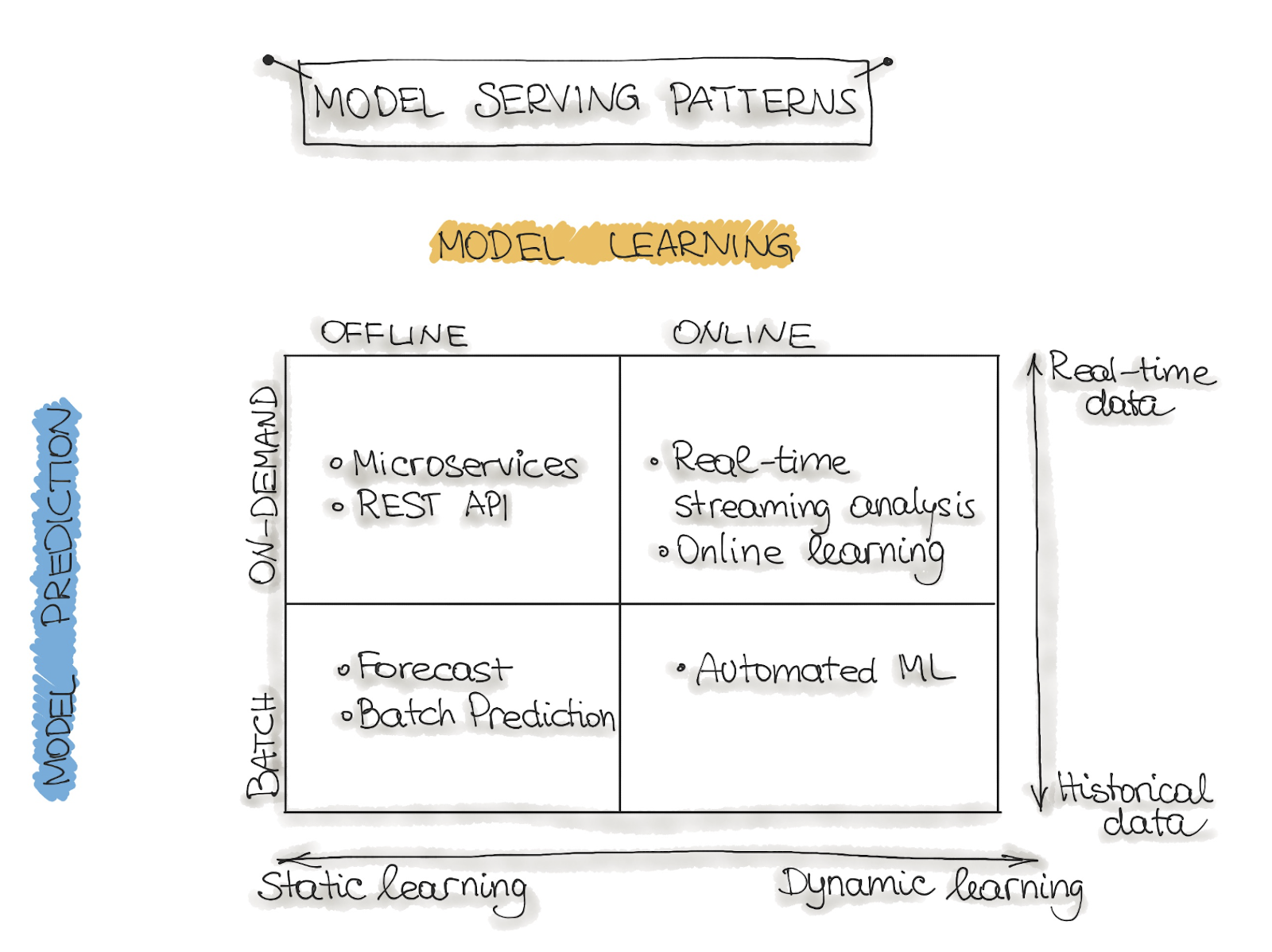
End-to-End ML Workflow Lifecycle
The end-to-end ML workflow is a comprehensive process that covers all stages of a machine learning project, from data preparation to model deployment and maintenance. It involves multiple steps, including:
- Data Preparation: Collecting, cleaning, and preprocessing data for model training.
- Model Training: Training and testing machine learning models using various algorithms and techniques.
- Model Evaluation: Evaluating the performance of trained models and selecting the best one.
- Model Deployment: Deploying the selected model in a production environment, making it accessible to end-users.
- Model Monitoring: Continuously monitoring the model's performance, identifying issues, and retraining or updating the model as needed.
- Model Maintenance: Maintaining and updating the model over time, ensuring it remains accurate and effective.
The end-to-end ML workflow is crucial for successful machine learning projects, as it ensures that models are properly trained, validated, and deployed to achieve their intended goals.
Three Levels of ML-based Software
Level 1: Data and Model
Focuses on data preparation, model training, and model evaluation. This level is concerned with building and training ML models.
Level 2: Data, Model, and Code
In addition to Level 1, this level involves writing code to deploy and integrate the ML model into a larger software system.
Level 3: Data, Model, Code, and Deployment Pipelines
The highest level of ML software, which includes all the previous levels and adds automated deployment pipelines to production.
Model serialisation formatting software summary:
MLOps Principles
Automation
- manual process
- ML pipeline automation
- CI/CD pipeline automation
- Continuous Integration (CI) extends the testing and validatin code and components by adding testing and validating data and models
- Continuous Delivery (CD) concerns with delivery of an ML training pipeline that automatically deploys an ML model prediction service
- Continuous Training (CT) is unique to ML systems which automatically retrain ML models for re-deployment
- Continuous Monitoring (CM) concerns with monitoring production data and model performance metrics, which are bound to business metrics
Experiments Tracking
Testing
Monitoring
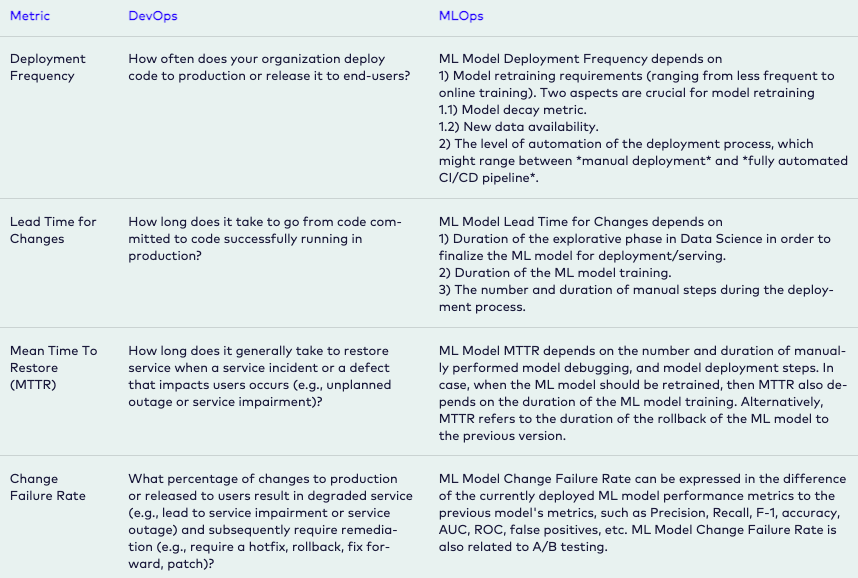
ML-based Software Delivery Metrics
MLOps and Model Governance
Model Governance
Model governance is a crucial aspect of Machine Learning Operations (MLOps) that ensures the integration of model governance processes throughout the ML lifecycle. It involves recording, auditing, validating, approving, and monitoring models to ensure compliance with legal and corporate requirements.
Importance of MLOps Governance
MLOps governance is essential for deploying ML models successfully. It provides fine-grained control and visibility into how ML models and pipelines operate in production, offering benefits such as:
- Elevated control and transparency
- Structured ability to trace activities
- Improved collaboration and decision-making
- Reduced risks and improved operational efficiencies
Model Governance Framework
A model governance framework encompasses the systems and processes in place to fulfill model governance needs for every operational ML model. It should be integrated into every stage of the ML lifecycle, covering both legal and corporate requirements.
Key Components of Model Governance
- Recording: tracking model development and deployment
- Auditing: monitoring model performance and identifying issues
- Validation: verifying model accuracy and reliability
- Approval: ensuring models meet regulatory and corporate standards
- Monitoring: tracking model performance and retraining as needed
Connection with MLOps
Model governance and MLOps are closely linked. The level of governance required depends on the number of models used and the regulations in the field. MLOps provides the infrastructure for implementing model governance processes, ensuring seamless integration and reuse of governance processes across multiple ML production pipelines.
Establishing a Model Governance Framework
To establish a model governance framework, it's essential to:
- Integrate model governance into every stage of the ML lifecycle
- Implement MLOps to provide the necessary infrastructure
- Define clear roles and responsibilities for model governance
- Establish processes for tracking, monitoring, and validating models
That is all for today!
See you tomorrow :)